Terror-Attack in Munich: Difference between revisions
From LINKS Community Center
Dinu (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Dinu (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|Use Cases Category=Real-world | |Use Cases Category=Real-world | ||
|Year=2016 | |Year=2016 | ||
|Publishing Organisation=Deutsche Hochschule der Polizei (DHPol) | |||
|Location=Munich, Germany | |Location=Munich, Germany | ||
|Event type=Amok, Terror | |Event type=Amok, Terror | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
|Type=Crowdsourcing, Social Media | |Type=Crowdsourcing, Social Media | ||
|Disaster Management Phase=After, During | |Disaster Management Phase=After, During | ||
|Used platforms=Twitter, X | |||
|Long description=Two days before the crime, he posted on Facebook inviting other teenagers to come to the fast-food restaurant. Around the afternoon of July 22, the young man visited the restaurant and killed five children and teenagers with a pistol. After that, the perpetrator left the scene and shot at other fleeing people, four of them died. Police tried to shoot the perpetrator to no avail. He hid in an apartment building, left it in the evening and shot himself in front of the police. Initially, the investigators assumed that the rampage was non-political. However, commissioned experts concluded that the crime was right-wing terrorism, as the perpetrator had selected his victims according to racist criteria. Moreover, the day was not chosen by chance, because five years earlier the extreme right-wing attacks in Oslo and Utøya by Anders Breivik took place. | |Long description=Two days before the crime, he posted on Facebook inviting other teenagers to come to the fast-food restaurant. Around the afternoon of July 22, the young man visited the restaurant and killed five children and teenagers with a pistol. After that, the perpetrator left the scene and shot at other fleeing people, four of them died. Police tried to shoot the perpetrator to no avail. He hid in an apartment building, left it in the evening and shot himself in front of the police. Initially, the investigators assumed that the rampage was non-political. However, commissioned experts concluded that the crime was right-wing terrorism, as the perpetrator had selected his victims according to racist criteria. Moreover, the day was not chosen by chance, because five years earlier the extreme right-wing attacks in Oslo and Utøya by Anders Breivik took place. | ||
|Involved Organisations=Police Munich | |||
|Use cases thematic=Collecting and Analysing Information from SMCS, Ensuring Credible Information, Making Information Accessible, Mobilising Volunteers | |Use cases thematic=Collecting and Analysing Information from SMCS, Ensuring Credible Information, Making Information Accessible, Mobilising Volunteers | ||
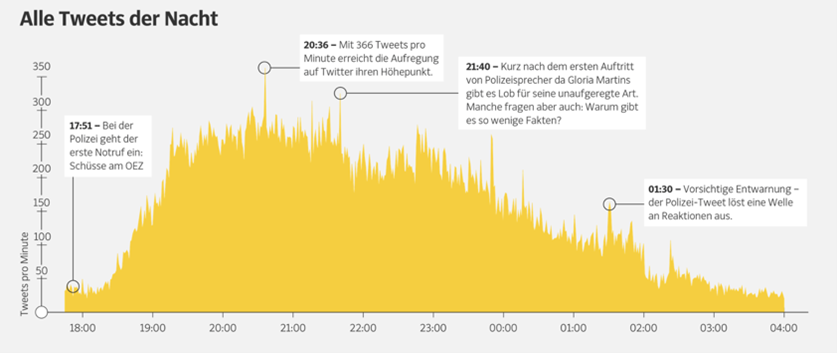
|Limitations=During the events, rumors are spread on social media, causing panic in the city, several people are injured. The police received 71 reports of alleged gunshots. Via the platform Periscope, users connect live from the crime scene to the Internet. This gives rise to speculation and false reports. The number of tweets on Twitter was increasing enormously. | |Limitations=During the events, rumors are spread on social media, causing panic in the city, several people are injured. The police received 71 reports of alleged gunshots. Via the platform Periscope, users connect live from the crime scene to the Internet. This gives rise to speculation and false reports. The number of tweets on Twitter was increasing enormously. | ||
|Additional links=https://www.bpb.de/kurz-knapp/hintergrund-aktuell/336826/vor-5-jahren-rechtsextremer-anschlag-in-muenchen/, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2016_Munich_shooting | |Worked well=Good communication with media by the Munich Police's press spokesperson | ||
|Additional links=https://www.bpb.de/kurz-knapp/hintergrund-aktuell/336826/vor-5-jahren-rechtsextremer-anschlag-in-muenchen /, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2016_Munich_shooting, | |||
'''Crisis Communication:''', | |||
[https://links.communitycenter.eu/index.php/ATTACKS_in_public_places Attacks in public places] | |||
|Other images=OEZ1.png | |Other images=OEZ1.png | ||
|Academic work addressing the incident=Test, Test | |Academic work addressing the incident=Test, Test | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:48, 29 November 2023
Created: 3 March 2023
Last edited: 29 November 2023
Last edited: 29 November 2023
On July 22, 2016, an 18-year-old man shot several people at a fast-food restaurant near the Olympic Shopping Centre in Munich.
Hazard:
Amok, TerrorYear:
2016Location:
Munich, GermanyScale:
CityInvolved Organisations:
Police MunichPublishing Organisation
Deutsche Hochschule der Polizei (DHPol)
Category
Real-world
Theme
Crowdsourcing, Social Media
Thematic
- Collecting and Analysing Information from SMCS
- Ensuring Credible Information
- Making Information Accessible
- Mobilising Volunteers
Disaster Management Phase
After, During