Difference between revisions of "Resilience Wheel"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <div class="bridging-page"> | |
| + | <div class="d-flex justify-content-between"> | ||
| + | <div style="padding-right: 2em"> | ||
| + | == Resilience Wheel == | ||
| + | === Navigating Social Media and Crowdsourcing in Disasters === | ||
| + | <div class="bp-section"> | ||
| + | Managing disasters is a complex task requiring the right knowledge, resources and experience within and across organisations. Social media and crowdsourcing may enable and alter these efforts if applied with sensitivity to the organization’s structure and procedures as well as the context in which efforts are targeted. | ||
| + | The Resilience Wheel supports initial discussions and assessments on how social media and crowdsourcing may support and challenge disaster management processes within and across organisations. It simplifies the complexity of managing disasters through technology into a set and subset of factors through which the link between disaster management and technology can be understood. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when using social media and crowdsourcing in management processes. It is a tool that helps to kick start holistic and context dependent conversations about potentials and challenges associated with using social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. It assists as a framework to map an organisations’ capacities to apply these technologies in disasters. | + | <div class="bp-section"> |
| + | ==== Description ==== | ||
| + | The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when using social media and crowdsourcing in management processes. It is a tool that helps to kick start holistic and context dependent conversations about potentials and challenges associated with using social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. It assists as a framework to map an organisations’ capacities to apply these technologies in disasters. | ||
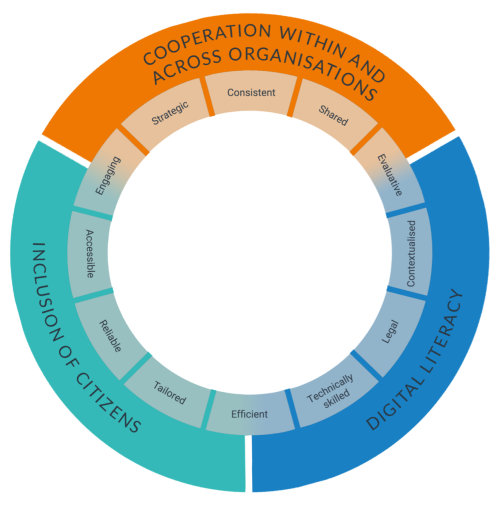
The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation. | The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | <div style="background-color: #ee7802; color: #fff; padding: 1em; margin-bottom: 2em;"> | ||
| + | '''Goal:''' To support initial discussions and assessments of the potential application of social media and crowdsourcing in disaster risk management processes | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div style="width:27em; border: 2px solid #ccc; padding: 1em; text-align:justify"> | ||
| + | ===== Profile ===== | ||
| + | '''Target group:''' Disaster management organisations | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Developers:''' The Copenhagen Centre for Disaster Research, University of Copenhagen and University College Copenhagen based on Arup/ Rockefeller Foundation, 2015 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Functions ===== | ||
| + | '''Communication tool:''' The conceptual base for a holistic discussion on how to apply social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Assessment tool:''' A base for a deeper assessment of current activities and uses of social media and crowdsourcing in disasters | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Value ===== | ||
| + | Promoting holistic policy and planning | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Status ===== | ||
| + | '''Timeframe:''' 2020 – 2022 | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Maturity level:''' ———— | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="d-flex justify-content-between mt-4"> | ||
| + | <div>[[File:Resilience Wheel.png|alt=A screenshot of the resilience wheel|center|frameless|link=https://cloud.links.communitycenter.eu/index.php/s/Pdj4wDtmFcgBmca|500px]]</div> | ||
| + | <div style="width:27em; border: 2px solid #ccc; padding: 1em; text-align:justify"> | ||
| + | ===== Sources ===== | ||
| + | '''Theory:''' The Wheel is based on a systematic review of all existing research linking social media and crowdsourcing with disaster risk management. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Empirics:''' The Wheel was co-designed with a wide range of disaster management organisations across Europe. Drivers and characteristics were based on and further informed through qualitative expert interviews across various hazard scenarios, organisation types and socio-political contexts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Practice:''' The Wheel is influenced by the City Resilience Framework developed by the Rockefeller Foundation and Arup for the 100 Resilient Cities Network. Yet, developed and translated to fit the specific aim of linking technology and management processes aiming at increasing disaster resilience. | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
<center>{{#widget:Button|url=https://cloud.links.communitycenter.eu/index.php/s/Pdj4wDtmFcgBmca|text=Access the Resilience Wheel|newtab=true}}</center> | <center>{{#widget:Button|url=https://cloud.links.communitycenter.eu/index.php/s/Pdj4wDtmFcgBmca|text=Access the Resilience Wheel|newtab=true}}</center> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 61: | ||
'''If you wish to test the Resilience Wheel or learn more, contact [mailto:anne.bach.nielsen@sund.ku.dk UCPH] or check out [https://links-project.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/3.1.pdf D3.1]''' | '''If you wish to test the Resilience Wheel or learn more, contact [mailto:anne.bach.nielsen@sund.ku.dk UCPH] or check out [https://links-project.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/3.1.pdf D3.1]''' | ||
| + | </div> | ||
__FORUM__ | __FORUM__ | ||
| + | __NOTITLE__ | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 6 October 2023
Resilience Wheel
Managing disasters is a complex task requiring the right knowledge, resources and experience within and across organisations. Social media and crowdsourcing may enable and alter these efforts if applied with sensitivity to the organization’s structure and procedures as well as the context in which efforts are targeted.
The Resilience Wheel supports initial discussions and assessments on how social media and crowdsourcing may support and challenge disaster management processes within and across organisations. It simplifies the complexity of managing disasters through technology into a set and subset of factors through which the link between disaster management and technology can be understood.
Description
The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when using social media and crowdsourcing in management processes. It is a tool that helps to kick start holistic and context dependent conversations about potentials and challenges associated with using social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. It assists as a framework to map an organisations’ capacities to apply these technologies in disasters.
The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation.
Goal: To support initial discussions and assessments of the potential application of social media and crowdsourcing in disaster risk management processes
Profile
Target group: Disaster management organisations
Developers: The Copenhagen Centre for Disaster Research, University of Copenhagen and University College Copenhagen based on Arup/ Rockefeller Foundation, 2015
Functions
Communication tool: The conceptual base for a holistic discussion on how to apply social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes.
Assessment tool: A base for a deeper assessment of current activities and uses of social media and crowdsourcing in disasters
Value
Promoting holistic policy and planning
Status
Timeframe: 2020 – 2022
Maturity level: ————
Sources
Theory: The Wheel is based on a systematic review of all existing research linking social media and crowdsourcing with disaster risk management.
Empirics: The Wheel was co-designed with a wide range of disaster management organisations across Europe. Drivers and characteristics were based on and further informed through qualitative expert interviews across various hazard scenarios, organisation types and socio-political contexts.
Practice: The Wheel is influenced by the City Resilience Framework developed by the Rockefeller Foundation and Arup for the 100 Resilient Cities Network. Yet, developed and translated to fit the specific aim of linking technology and management processes aiming at increasing disaster resilience.
If you wish to test the Resilience Wheel or learn more, contact UCPH or check out D3.1