Resilience Wheel: Difference between revisions
Kiehl (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Kiehl (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tag: visualeditor |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when | The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when using social media and crowdsourcing in management processes. It is a tool that helps to kick start holistic and context dependent conversations about potentials and challenges associated with using social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. It assists as a framework to map an organisations’ capacities to apply these technologies in disasters. | ||
The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation. | The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation. | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 7 December 2022
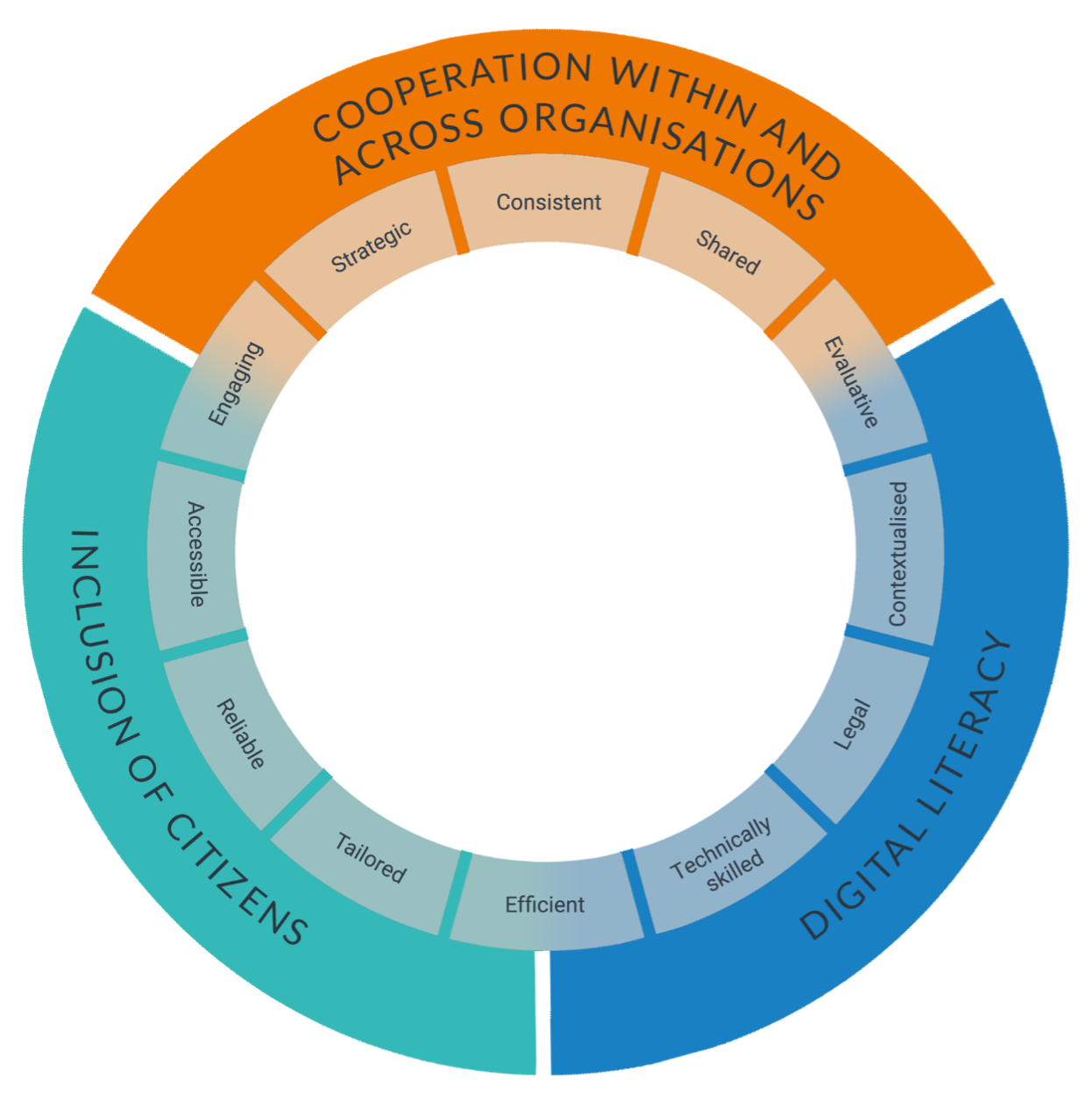
The Resilience Wheel is a strategic tool for discussing and assessing what authorities, NGOs and private sector organizations working with disasters need to consider when using social media and crowdsourcing in management processes. It is a tool that helps to kick start holistic and context dependent conversations about potentials and challenges associated with using social media and crowdsourcing in disaster management processes. It assists as a framework to map an organisations’ capacities to apply these technologies in disasters.
The Wheel consists of two layers: a set of drivers that reflect the most important focal points to alter resilience-building through social media and crowdsourcing. Connected to each driver is a set of characteristics that describe the needed qualities for building disaster resilience through social media and crowdsourcing in an organisation.
If you wish to test the Resilience Wheel or learn more, contact UCPH or check out D3.1